Chip发表中国科学技术大学郭国平、雒超团队最新成果:面向量子计算的低温CMOS模型库与600 MHz低温时钟发生器
FUTURE远见| 2024-02-18
Future|远见
Future|远见future选编
近日,中国科学技术大学郭国平、雒超团队以「Cryo-CMOS modeling and a 600 MHz cryogenic clock generator for quantum computing applications」为题在Chip上发表研究论文,建立了低至4 K温度下的CMOS模型库,并基于此开发了一款适用于4 K温度下的600 MHz低温时钟发生器。该系统已采用中芯国际 180 nm工艺成功流片。第一作者为薛棋文、张元可,通讯作者为雒超。本文为特刊(Cryogenic Chips)文章之一,此特刊为Chip发起的首个特刊。Chip是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,是入选了国家高起点新刊计划的「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。

稀释制冷机中量子比特状态的控制和读出需要将极低温下的量子比特通过同轴线连接到室温下的商用仪器来实现。然而,随着量子比特数目的增加,同轴线数量的增加以及引入的热泄露和延迟给量子比特的调控带来了巨大的挑战¹。为了应对这些问题,图1展示的低温量子比特测控电路成为大规模量子计算的研究热点²。
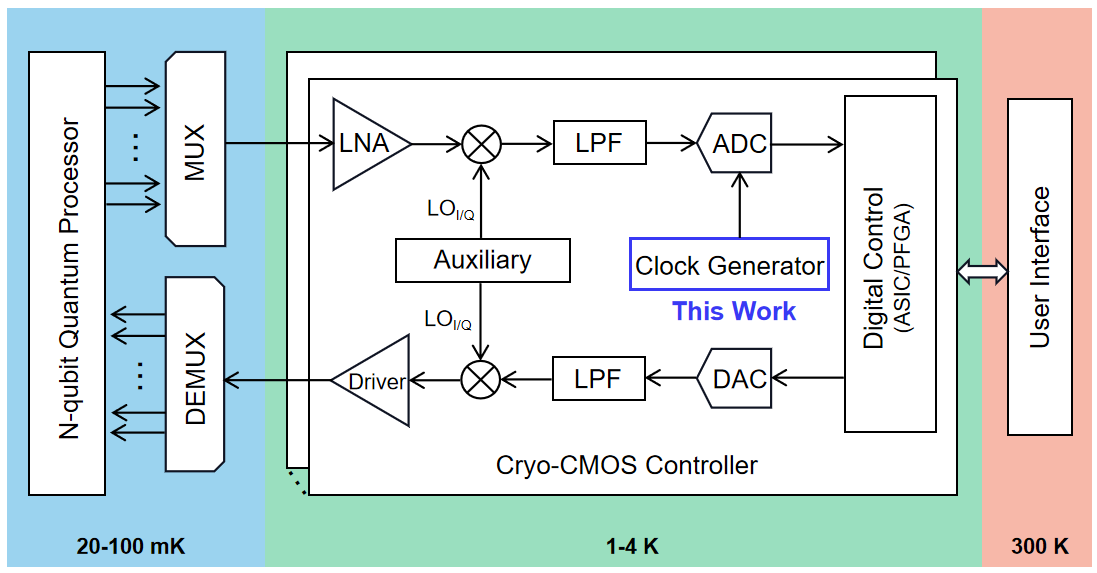
图1 | 低温量子比特测控系统架构。
此外,互补金属氧化物半导体(Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor,CMOS), CMOS器件的电学特性在低温环境中表现出显著的变化,因此需要对CMOS器件进行低温表征和模型建立,以协助低温电路设计。在前期对低温CMOS的表征与器件物理研究的基础上³⁻⁵,本工作中研究者成功开发了SMIC 180 nm CMOS仿真模型并利用机器学习的方式进行参数优化,如图2所示。
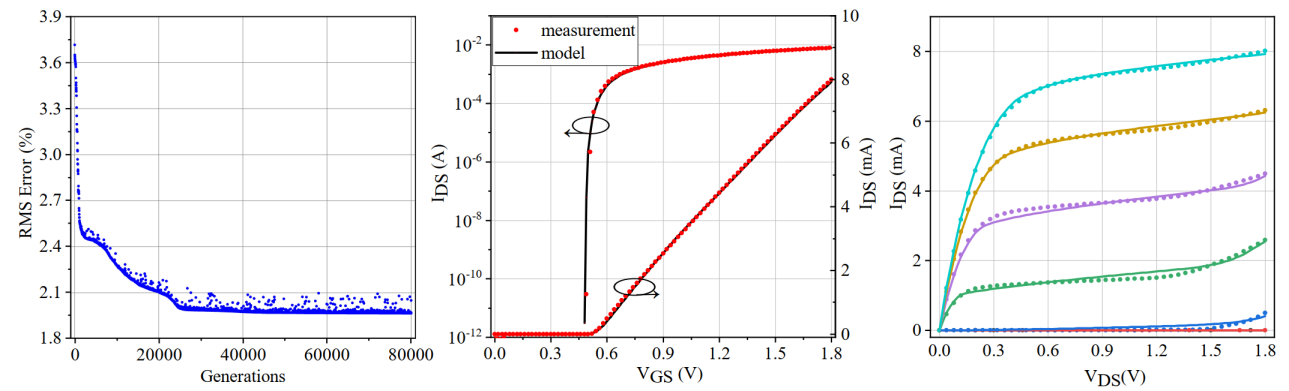
图2 | 低温CMOS器件模型建立。
基于上述低温CMOS模型,研究者完成了图3所示的低温时钟发生器的设计工作。所设计的时钟发生器在4 K温度下可输出450 MHz~850 MHz的时钟信号,如图4所示,在输出频率600 MHz时,实现了−95.53 dBc/Hz@10kHz、−102.73 dBc/Hz的噪声性能,RMS Jitter为4.8 ps。该时钟发生器能够为可扩展量子计算机的控制和读出电子设备提供稳定的时钟信号。
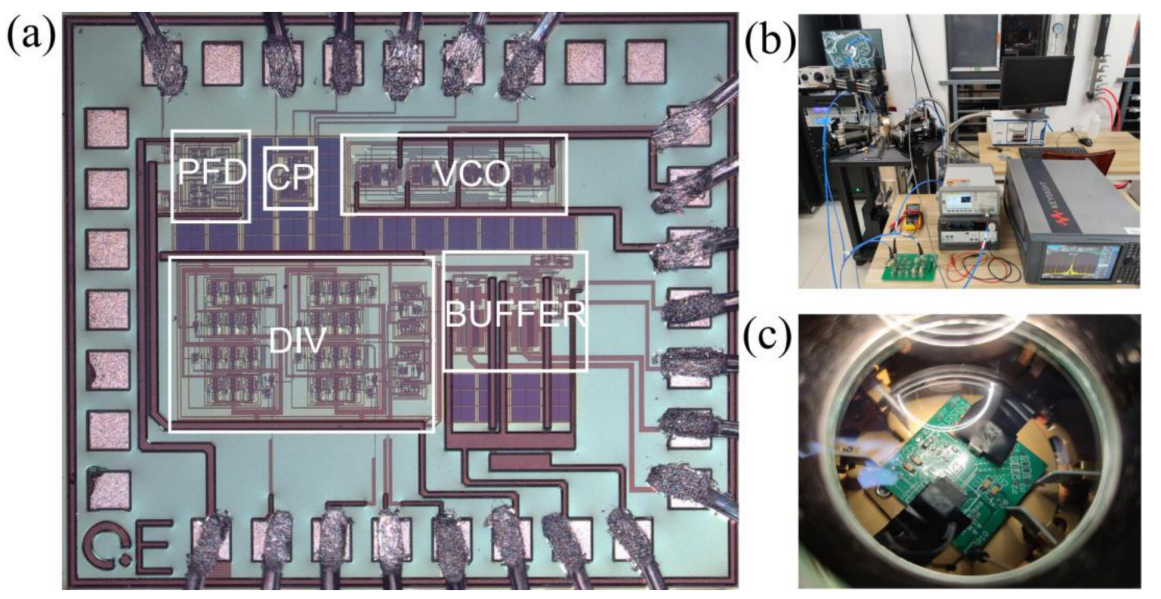
图3 | 低温时钟产生系统与测试环境。
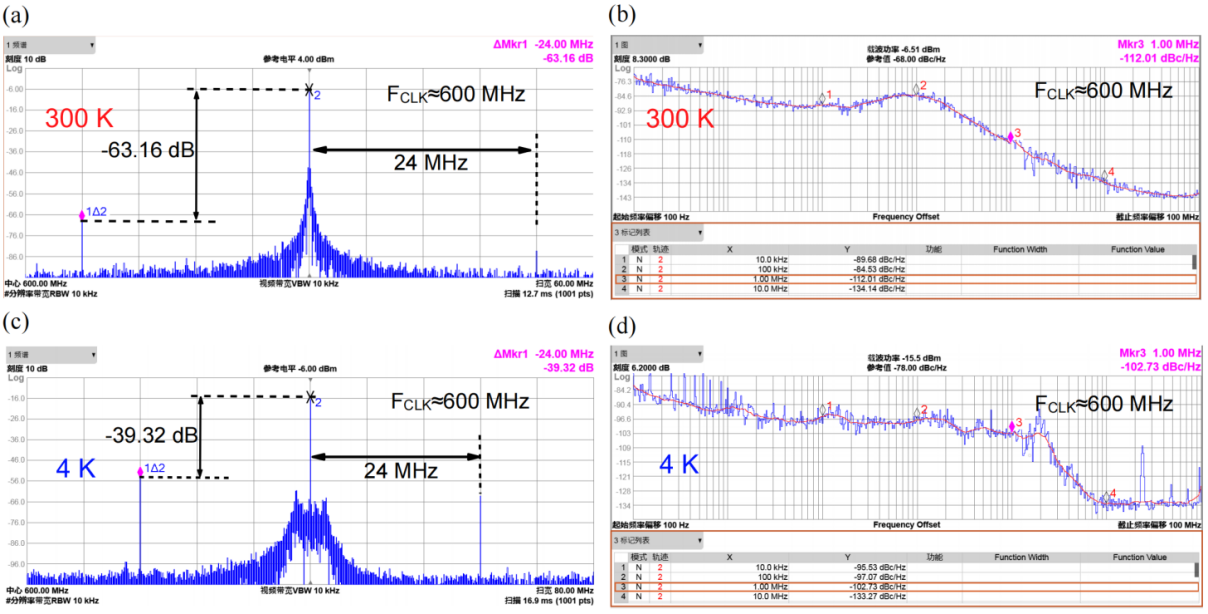
图4 | 时钟产生系统测试结果。
Cryo-CMOS modeling and a 600 MHz cryogenic clock generator for quantum computing applications
Quantum bits (qubits) are operated in an ultra-low temperature environment provided by a dilution refrigerator and are connected to the classical control interface operating at room temperature. However, as the number of qubits grows towards thousands and millions, the corresponding increasing number of long cables introduces challenges¹, including heat leakage and time delays, which significantly impact the temperature stability inside the dilution refrigerator and complicate the measurement process. To overcome this bottleneck, a cryogenic electronic interface that operates in close proximity to the quantum processor has been proposed (Fig. 1) and has become a hot topic the field of large-scale quantum computing².
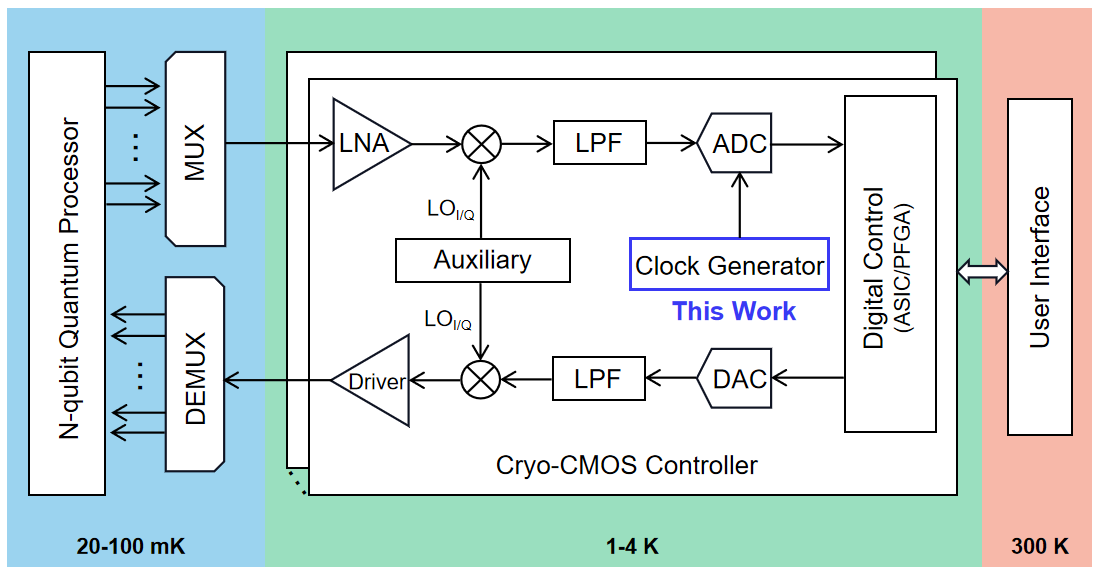
Fig. 1 | Simplified block diagram of the cryo-CMOS controller for the control and readout of qubits.
In this paper, 180 nm CMOS transistors are characterized and modeled down to 4 K³⁻⁵(Fig. 2). Based on the proposed model, a 180 nm process clock generator for the control and read-out electronics of qubits is presented (Fig. 3). At 4 K, the clock generator exhibits an output frequency range of 450-850 MHz (Fig. 4). At an output frequency of 600MHz, it achieves a phase noise of −95.53 dBc/Hz at 10 kHz offset, −102.73 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset, with an RMS Jitter <4.8 ps, which is suitable for providing a stable clock signal for the control and readout electronics of scalable quantum computers.
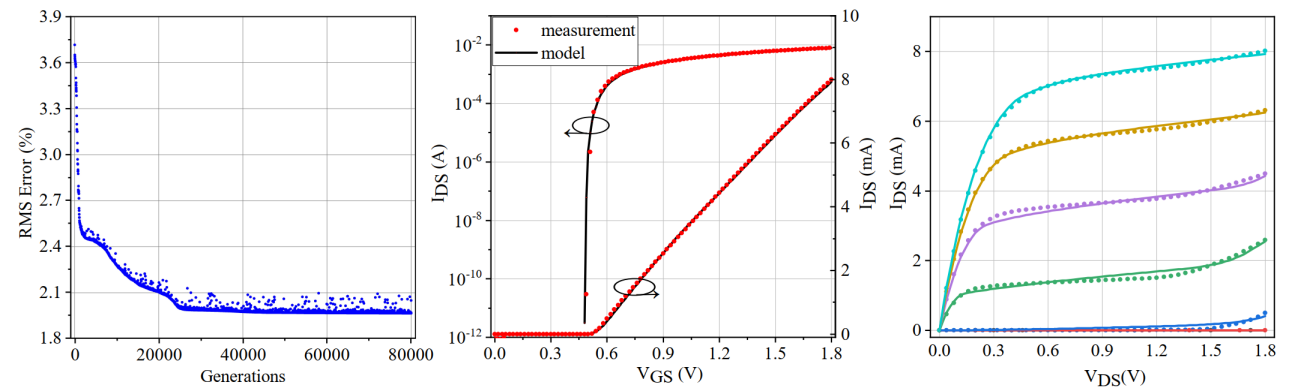
Fig. 2 | Cryo-CMOS characterization and modeling.
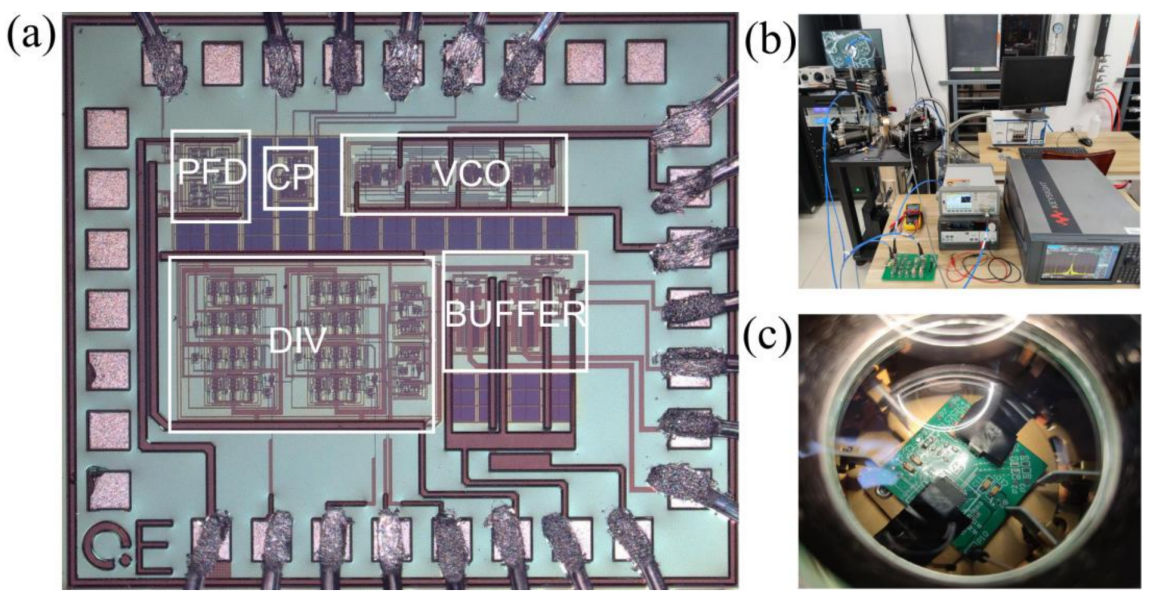
Fig. 3 | Details of measurement.
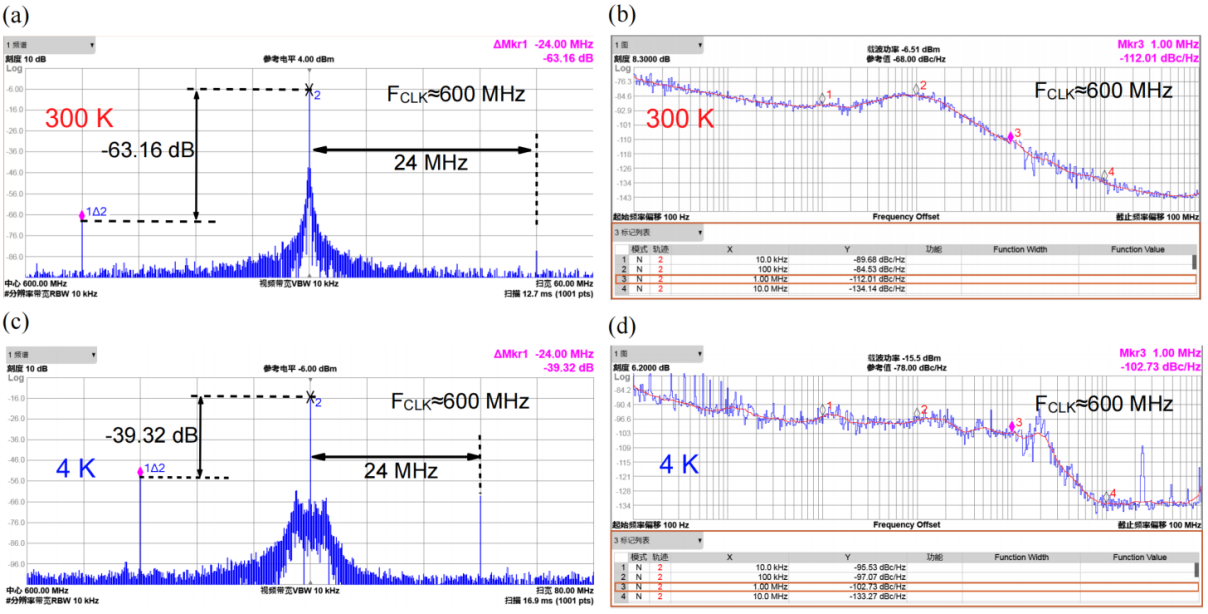
Fig. 4 | Measured spectrum and phase noise of the PLL.
参考文献:
1. Patra, B. et al. Cryo-CMOS circuits and systems for quantum computing applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53, 309–321 (2018).
2. Guevel, L. L. et al. A 110 mK 295 μW 28 nm FDSOI CMOS quantum integrated circuit with a 2.8 GHz excitation and nA current sensing of an on-chip double quantum dot. In 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 306–308 (IEEE, 2020).
3. Zhang, Y. et al. Characterization and modeling of native MOSFETs down to 4.2 K. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 68, 4267-4273 (2021).
4. Y. Chen et al. Compact modeling of quantum transport in 55-nm MOSFETs at cryogenic temperatures. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 44, 1392-1395 (2023).
5. Y. Zhang et al. Cryogenic hysteresis in 110 nm bulk silicon MOSFETs for capacitorless memory applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 44, 1543-1546 (2023).
论文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chip.2023.100065
作者简介

薛棋文,中国科学技术大学硕士研究生(已毕业),主要研究方向为面向量子比特调控的锁相环研究和设计。
Qiwen Xue received his Master's degree from the University of Science and Technology of China in 2022. His research interests include research and design of phase-locked loops for quantum bit control.

张元可,中国科学技术大学物理系博士研究生。研究兴趣包括低温CMOS器件物理与模型建立。
Yuanke Zhang is currently a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China. His research interests include cryogenic semiconductor device physics and cryo-CMOS modeling.

雒超,中国科学技术大学物理系副研究员。于中国科学技术大学获电子科学与技术学士学位(2014年)和博士学位(2019年)。他的研究兴趣包括低温电子学和用于量子计算的低温下电路设计。
Chao Luo is an associate research professor in the Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China. He received his B.S. degree in 2014 and Ph.D. degree in 2019 from University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China. His research interests include cryogenic electronics and the electronic interface operating at cryogenic temperature for quantum computing applications.

郭国平,中国科学技术大学物理系教授。于中国科学技术大学获物理学学士学位(2000年)和博士学位(2005年)。他的研究兴趣包括低温电子学和量子计算。
Guoping Guo is a professor at University of Science and Technology of China. He received his B. S. degree in 2000 and Ph. D. degree in 2005 from University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China. His research interests focus on cryogenic electronics and quantum computing.
关于Chip
Chip(ISSN:2772-2724,CN:31-2189/O4)是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,已入选由中国科协、教育部、科技部、中科院等单位联合实施的「中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目」,为科技部鼓励发表「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。
Chip期刊由上海交通大学出版,联合Elsevier集团全球发行,并与多家国内外知名学术组织展开合作,为学术会议提供高质量交流平台。
Chip秉承创刊理念: All About Chip,聚焦芯片,兼容并包,旨在发表与芯片相关的各科研领域尖端突破性成果,助力未来芯片科技发展。迄今为止,Chip已在其编委会汇集了来自14个国家的70名世界知名专家学者,其中包括多名中外院士及IEEE、ACM、Optica等知名国际学会终身会士(Fellow)。
Chip第二卷第四期已于2023年12月在爱思维尔Chip官网以金色开放获取形式(Gold Open Access)发布,欢迎访问阅读本期最新文章。
爱思唯尔Chip官网:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/chip




