Chip发表清华大学段路明团队最新成果:基于超导量子电路的可调频微波量子光源
FUTURE远见| 2023-12-04
Future|远见
Future|远见future选编

单光子态无论是对于基础研究还是实际应用都有着十分重要的作用²。比如在微波频段,飞行单光子态可以被用来实现远程超导量子芯片之间的连接,有望大大增强超导量子计算的可扩展性³。在本工作中,研究者利用超导量子电路实现了一个调频范围为200 MHz的微波单光子源,并生成了包括时间相位(time-bin)编码的光量子比特在内的各种非经典量子态。
 图1 | 微波量子光源的光学照片以及测量线路的示意图。
图1 | 微波量子光源的光学照片以及测量线路的示意图。如图1所示,光源由通过超导量子干涉器(SQUID)调频的共面波导谐振腔和transmon 超导量子比特耦合组成,利用拉曼跃迁可以将量子比特的第二激发态转移到基态并同时在谐振腔内生成单个光子⁴,再经由谐振腔与传输线的耦合产生飞行的单光子态。由于生成的单光子态频率和腔频相同,所以可以调节通过SQUID的磁通大小从而改变生成的光子频率,如图2所示。

图2 | 可调频的单光子源。a, 腔频与磁通的关系曲线;b, 单光子态的电压分布图;c, 腔的内部损耗与效率随频率的变化曲线。
利用time-bin编码的方法,尽管光源本身的效率有限,研究人员仍然可以利用其生成具有高保真度的飞行光量子比特⁵。经过如图3a中的脉冲序列,研究人员可以把处于的量子比特转变为飞行光量子比特态,其中和分别表示飞行的单光子态位于前模式(early mode)和后模式(late mode)。除此之外,利用类似的脉冲序列,研究人员也可以制备量子比特和光量子比特之间的纠缠贝尔态,如图3d所示。在实验中,研究人员测量了不同频率下飞行光量子态的保真度,
由于time-bin编码本身对于光子的损耗不敏感,可以发现不同频率的飞行光量子态的保真度并没有随着频率的变化而降低,如图3e所示。
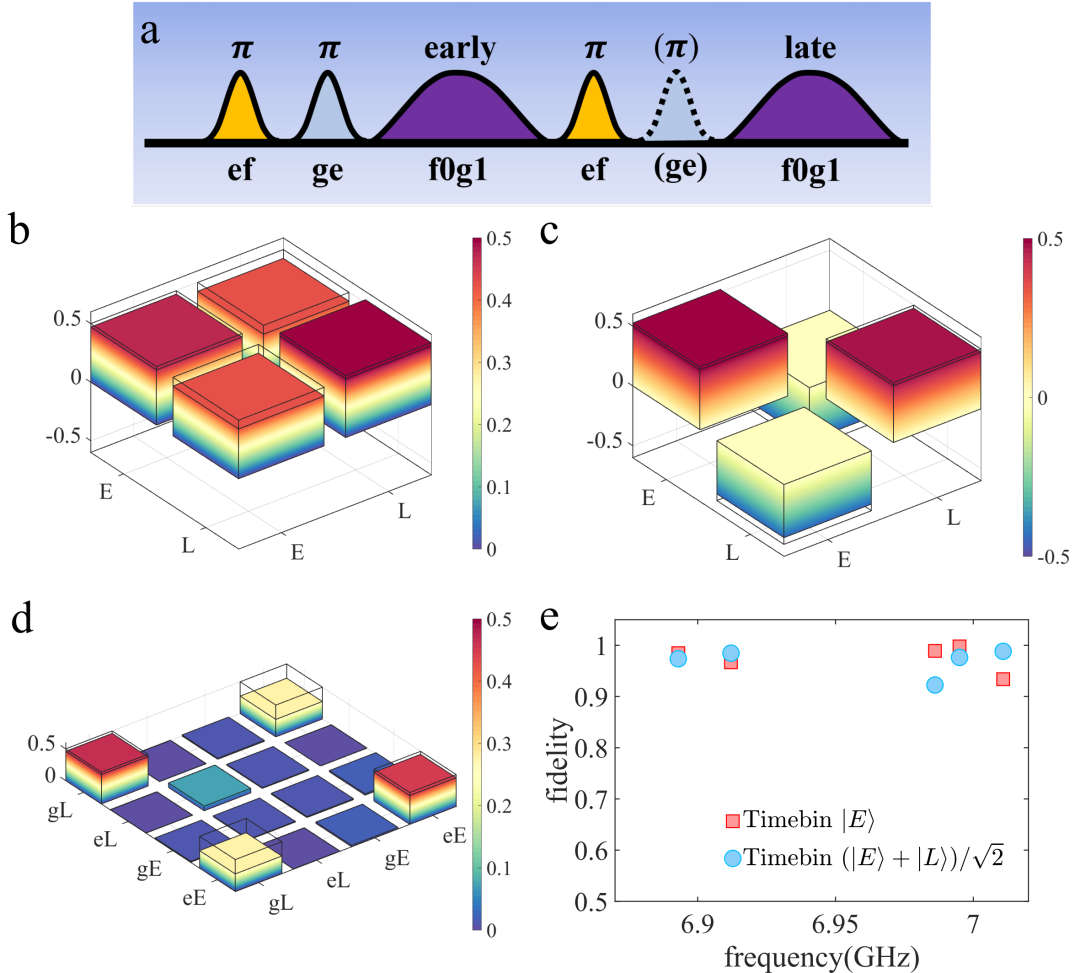
图3 | 可调频的光量子比特。a, 生成光量子比特的脉冲时序;b, c, 分别是和的密度矩阵;d, 贝尔纠缠态的密度矩阵;e, 不同频率下的光量子态的保真度。
综上所述,这篇文章实现了一个可以调频的微波单光子源并生成了包括单光子态,time-bin编码的飞行光量子态以及贝尔纠缠态等在内的非经典态。这种单光子源在量子网络以及中等规模量子计算的搭建中具有着广泛的应用。
Frequency-tunable microwave quantum light source based on superconducting quantum circuits¹
In this work, researchers report an experimental realization of a frequency-tunable single-photon source in the microwave regime. Based on superconducting quantum circuits, our device can generate frequency-tunable microwave single photons within a range of more than 200 MHz. Additionally, the photon source can be programmed to generate time-bin encoded photonic qubits and qutrits with high fidelities, even with a limited quantum efficiency of the photon generation process. This work demonstrates great potential for application in the field of microwave quantum networks and quantum information processing².
A single photon source is essential for implementing many quantum information processing protocols. For example, in the microwave regime, flying microwave single photons can bridge remote superconducting quantum chips to realize distributed quantum computing³. In this aspect, a single photon source that emits single photon pulses with tunable frequency is preferred to bridge the possible spectral mismatches of distant quantum nodes.
As illustrated in Fig. 1, the device composes a coplanar waveguide resonator coupled to a transmon qubit. A superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) is embedded in the cavity to tune the resonator frequency. Researchers use the resonator-assisted Raman process to generate propagating single photons, wherein the qubit population in the second excited state is transferred as a single photon in the resonator via the ‘f0g1’ transition⁴. By varying the flux bias of the SQUID, researchers could change the frequency of the single photon, as shown in Fig. 2.
In the presence of inefficiency of the frequency-tunable single-photon source, time-bin encoding can be used to realize propagating photonic qubits with high fidelity⁵. Using pulse sequence in Fig. 3a, if the transmon qubit of the photon source is prepared in a superposition state,after the pulse sequence one would have, where() represents that the single photon is in the early(late) mode. Using similar pulse sequence, a Bell state between the transmon qubit and the propagating photonic qubit can be generated, as illustrated in Fig. 3d. In the experiment, researchers measure the fidelity of the time-bin qubit at different frequencies, as presented in Fig. 3e. The time-bin encoding scheme ensures that the fidelity of the propagating qubit is insensitive to the quantum efficiency of the light source.
In conclusion, researchers realize a frequency-tunable quantum light source in the microwave regime. Hereafter, researchers showcase the generation of single photons, time-bin encoded propagating photonic qubits and qutrits. This work demonstrates a quantum light source in the microwave regime which has broad application in the future quantum network and modular quantum computing.
参考文献:
1. Li, Y. et al. Frequency-tunable microwave quantum light source based on superconducting quantum circuits. Chip 2, 100063 (2023).
2. Kimble, H. J. The quantum internet. Nature 453, 1023-1030 (2008).
3. Zhong, Y. et al. Deterministic multiqubit entanglement in a quantum network. Nature 590, 571-575 (2021).
4. Pechal, M. Microwave-controlled generation of shaped single photons in circuit quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. X 4, 041010 (2014).
5. Ilves, J. et al. On-demand generation and characterization of a microwave time-bin qubit. npj Quantum Inf. 6, 34 (2020).
论文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2709472323000266
作者简介

李严,本科毕业于清华大学物理系,目前在清华大学交叉信息研究院攻读博士学位,研究方向主要为circuit QED,超导量子计算以及相关器件。
Yan Li obtained his bachelor in the department of physics, Tsinghua University. Now he is a PhD student in IIIS, Tsinghua University. He is working on circuit QED, superconducting quantum computation and related devices.

王志凌,2022年6月于清华大学交叉信息研究院获得博士学位,目前于日本理化学研究所作为博士后研究员,研究方向主要为circuit QED下的量子光学,以及其在量子计算中的相关应用。
Zhiling Wang obtained his PhD degree in IIIS, Tsinghua University in June 2022. Now he is working as a postdoctoral researcher at Riken, Japan. He is working on quantum optics under circuit QED, and corresponding applications in quantum computing.

鲍增晖,本科毕业于南京大学物理学院,目前在清华大学交叉信息研究院攻读博士学位,研究方向主要为基于超导量子线路的量子信息处理和量子网络相关器件。
Zenghui Bao obtained his bachelor in the School of Physics, Nanjing University. Now he is a PhD student in IIIS, Tsinghua University. He is working on quantum information processing based on superconducting circuits, and quantum network related devices.

张宏毅,清华大学交叉信息研究院副研究员。2014年博士毕业于中国科学院半导体研究所,之后进入清华大学交叉信息研究院工作。主持和参与多项国家自然科学基金、科技部重大专项等项目。研究方向为超导量子计算和量子信息处理,微波量子光学,近年来Physical Review Letters,Nature Communications,Science Advances等期刊发表文章二十余篇。
Hongyi Zhang is an associate research fellow at the Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences of Tsinghua University. He received his PhD from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2014 and later joined the Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences of Tsinghua University. He has led and participated in many projects, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Major Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology. His research interests include superconducting quantum computing and quantum information processing, microwave quantum optics. He has published more than 20 articles in journals such as Physical Review Letters, Nature Communications, Science Advances in recent years.

段路明,清华大学姚期智讲座教授、清华大学基础科学讲席教授。长期从事量子计算机和量子网络方向的研究。他曾获得中科院院长特别奖、全国优秀博士论文、饶毓泰基础光学奖、霍英东青年研究奖、中科院百人计划、中科院自然科学二等奖和国家自然科学二等奖。2004年获美国斯隆研究奖,2005年获海外华人物理学会杰出研究奖,2009年当选美国物理学会会士。完成了量子信息领域一些开创性的工作,提出实现长距离量子通信网络的量子中继方案,被国际同行誉为“DLCZ”(Duan-Lukin-Cirac-Zoller)方案,为该领域的奠基性方案。段教授提出通过量子网络互联进行规模化量子计算的方案,为近期离子量子计算的规模化发展奠定了理论基础,并受邀在物理学权威期刊《现代物理评论》上撰写此方向的综述。段教授在物理学著名学术期刊发表论文180余篇(其中《物理评论快报》50余篇,《自然》8篇,《科学》3篇,《自然》、《科学》子刊10余篇),共被引用37,000多次。
Luming Duan, C.C. Yao Professor and Fundamental Science Chair Professor of Tsinghua University. His research interests include quantum computing and quantum networks. He has received a number of recognitions, including the Special Award of the President of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation Award, the Rao Yutai Basic Optics Award, the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Second Prize of Natural Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Second Prize of Natural Science of China, the A. P. Sloan Fellowship and the Outstanding Young Researcher Award from the Overseas Chinese Physics Association. He was elected a fellow of the American Physical Society in 2009. He is well known for a number of innovative proposals for the implementation of quantum information, including the "DLCZ" (Duan-Lukin-Cirac-Zoller) scheme for realizing long-distance quantum communication. He has published 180 papers in refereed journals (including 50s in PRL, 8 in Nature, 3 in Science, and one in Reviews of Modern Physics) with more than 37,000 total citations.
关于Chip
Chip(ISSN:2772-2724,CN:31-2189/O4)是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,已入选由中国科协、教育部、科技部、中科院等单位联合实施的「中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目」,为科技部鼓励发表「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。
Chip期刊由上海交通大学出版,联合Elsevier集团全球发行,并与多家国内外知名学术组织展开合作,为学术会议提供高质量交流平台。
Chip秉承创刊理念: All About Chip,聚焦芯片,兼容并包,旨在发表与芯片相关的各科研领域尖端突破性成果,助力未来芯片科技发展。迄今为止,Chip已在其编委会汇集了来自14个国家的70名世界知名专家学者,其中包括多名中外院士及IEEE、ACM、Optica等知名国际学会终身会士(Fellow)。
Chip第二卷第四期将于2023年12月在爱思维尔Chip官网以金色开放获取形式(Gold Open Access)发布,欢迎访问阅读本期最新文章。
爱思唯尔Chip官网:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/chip




