Chip10 Science | 基于深度学习的高空间分辨率片上快速光谱成像
FUTURE远见| 2024-04-11
Future|远见
Future|远见future选编

近日,清华大学黄翊东、崔开宇团队以「Deep-learning-based on-chip rapid spectral imaging with high spatial resolution」¹为题在Chip上发表研究论文,提出将深度展开神经网络ADMM-net与基于自由形状的超表面光谱成像芯片相结合,实现了高空间分辨率的片上快速光谱成像,并消除了光谱图像的马赛克现象。本文第一作者为杨家伟,通讯作者为崔开宇和黄翊东。Chip是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,是入选了国家高起点新刊计划的「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。

光谱成像扩展了传统彩色相机的概念,可以在多个光谱通道捕获图像,在遥感、精准农业、生物医学、环境监测和天文学等领域得到了广泛应用。传统的基于扫描方式的光谱相机存在采集速度慢、体积大、成本高等问题。基于超表面宽带调制和计算光谱重建的片上光谱成像为实现消费级的便携式光谱相机提供了一种很有前景的方案。图1展示了超表面光谱成像芯片的基本结构,由硅基超表面层和带有微透镜的CMOS图像传感器组成,超表面层包含了360 × 440个超表面单元,每个超表面单元对应于成像空间中的一点,入射光经过每个超表面单元的频谱调制后被下方的传感器像素所探测。任一点处的光谱可以由该点附近的若干个光强探测值重建得到,重建过程对应于求解一个欠定线性方程组。现有的光谱图像重建算法需要通过逐点光谱重建来得到整个数据立方,存在计算耗时长和重建图像存在马赛克现象的问题。
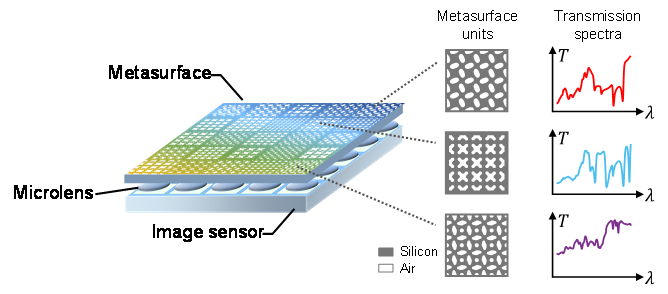 图1 | 超表面光谱成像芯片的结构示意图。
图1 | 超表面光谱成像芯片的结构示意图。由于不同的超表面单元具有不同的光谱调制特性,整个超表面光谱成像芯片在不同波长下具有不同的空间调制特性,因此本文受启发于编码孔径快照式光谱成像算法,采用深度展开神经网络ADMM-net²进行光谱图像的快速重建,其基本架构如图2所示。网络包含K=12个阶段,每个阶段都包含线性变换W(·)和降噪卷积神经网络(通常采用U-net结构)两部分。网络的输入是包含所有超表面单元光谱调制特性的传感矩阵Φ和测量图像y,输出为重建的光谱图像数据立方。
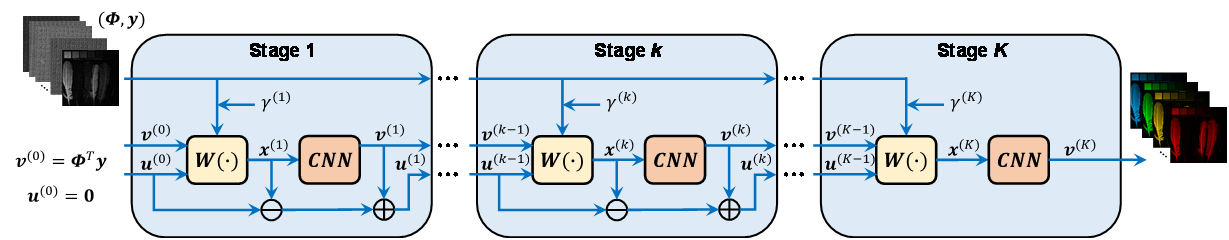 图2 | 深度展开神经网络ADMM-net的基本架构。
图2 | 深度展开神经网络ADMM-net的基本架构。图3展示了利用超表面光谱成像芯片对标准色卡进行实际成像测量后,采用不同算法重建数据立方的结果。从RGB伪彩色图中可以看出,ADMM-net的图像细节重建效果显著优于采用传统的CVX算法进行逐点光谱重建的结果,有效消除了图像的马赛克现象。并且,相比于传统迭代算法GAP-TV³和端到端神经网络λ-net⁴的重建结果,ADMM-net的光谱重建准确性也更优。此外,采用ADMM-net进行单次重建仅需18毫秒,而逐点光谱重建则需要4854秒,本工作在重建速度上实现了约5个数量级的提升。
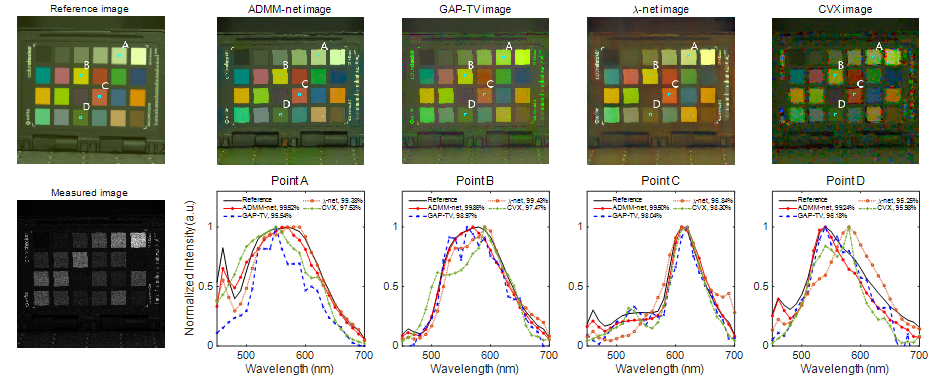 图3 | 对标准色卡进行实际成像测量后,利用不同算法进行光谱图像重建的结果。
图3 | 对标准色卡进行实际成像测量后,利用不同算法进行光谱图像重建的结果。进一步,本工作利用ADMM-net实现了对户外驾驶场景的实时光谱成像,如图4所示,光谱成像速率达到约36帧/秒。从RGB伪彩色图中可见,车辆的色彩重建准确性较好;并且,从第20、100帧图像中的采样点A和B的重建光谱来看,天空和白色车辆的光谱具有明显的差异,有望解决自动驾驶场景中的同色异谱识别问题,避免相撞事故的发生。此外,具有视频帧率的高空间分辨快速光谱成像,也展示出实时光谱成像芯片在机器视觉领域的巨大应用潜力。
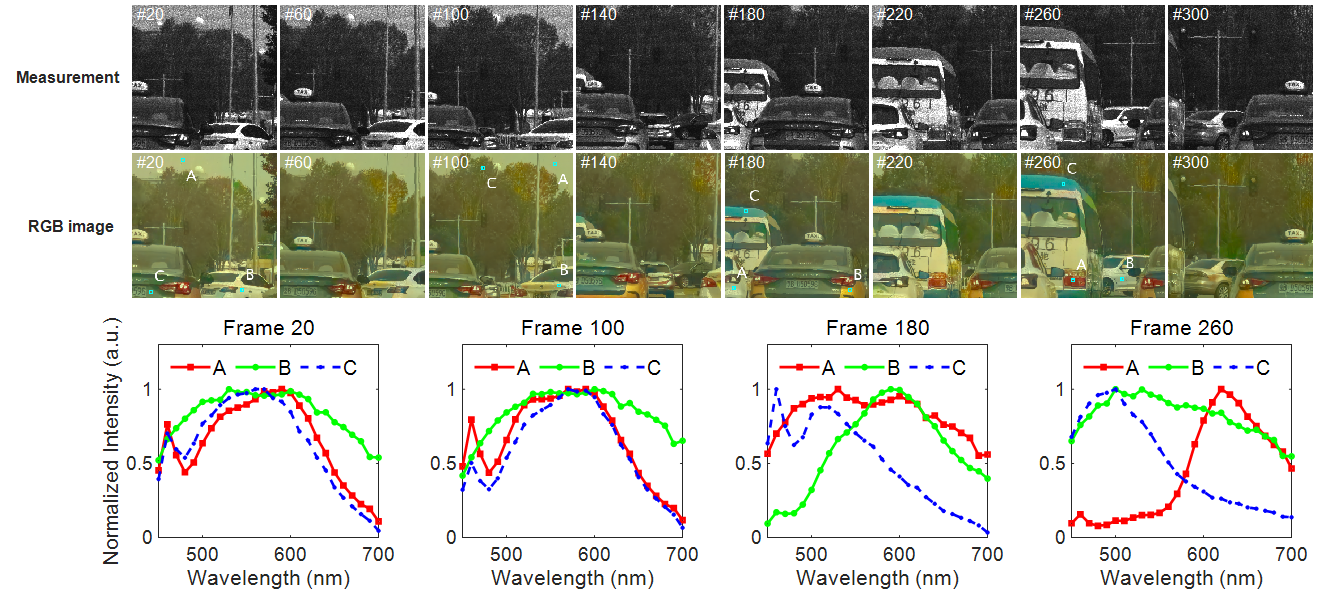 图4 | 户外驾驶场景的实时光谱成像结果。
图4 | 户外驾驶场景的实时光谱成像结果。Deep-learning-based on-chip rapid spectral imaging with high spatial resolution¹
Spectral imaging extends the concept of traditional color cameras to capture images across multiple spectral channels and has broad application prospects. Conventional spectral cameras based on scanning methods suffer from low acquisition speed and large volume. On-chip computational spectral imaging based on metasurface filters provides a promising scheme for portable applications, but endures long computation time for point-by-point iterative spectral reconstruction and mosaic effect in the reconstructed spectral images.
Since different metasurface units have different spectral modulation characteristics, the whole metasurface spectral imaging chip has different spatial modulation characteristics at different wavelength channels. Therefore, inspired by the reconstruction algorithms in coded aperture spectral imaging, this paper adopts the deep unfolded neural network ADMM-net for the fast reconstruction of spectral images. The network consists of 12 stages, where each stage contains a linear projection W(·) and a CNN denoiser (usually U-net structure). The input of the network is the sensor matrix Φ and the measurement image y, and the output is the reconstructed data cube.
Researchers generate the spectral image reconstruction results using different algorithms for a standard color board. It can be seen from the post-colored RGB images, the performance of image detail reconstruction using ADMM-net is significantly better than that using traditional point-by-point CVX spectral reconstruction algorithm, effectively eliminating the mosaic phenomenon in the spectral image. Moreover, the spectral reconstruction accuracy of ADMM-net is better than that of the traditional iterative algorithm GAP-TV and the end-to-end neural network λ-net. In addition, the single reconstruction using ADMM-net takes only 18 milliseconds while the point-by-point spectral reconstruction takes 4854 seconds, which achieves about 5 orders of magnitude of improvement in the reconstruction speed.
Furthermore, real-time spectral imaging of the outdoor driving scene was realized by using ADMM-net, and the spectral imaging rate reached about 36 frames per second. It can be seen from the post-colored RGB images that the reconstructed color accuracies of cars are quite good. Moreover, it can be seen from the reconstructed spectra of the sampling point A and B in the 20th and 100th frame, the concolorous sky and white cars can be distinguished via their spectra which is expected to solve the problem of metamerism recognition in the automatic driving scene and avoid collision accidents. In addition, the rapid spectral imaging with high spatial resolution and video frame rate also demonstrates the great application potential of real-time spectral imaging chips in the field of machine vision.
参考文献
1. Yang, J. et al. Deep‐learning based on‐chip rapid spectral imaging with high spatial resolution. Chip 2, 100045 (2023).
2. Yang, J. et al. Ultraspectral imaging based on metasurfaces with freeform shaped meta‐atoms. Laser Photonics Rev. 16, 2100663 (2022).
3. Meng, Z., Jalali, S. & Yuan, X. Gap-net for snapshot compressive imaging. Preprint in https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2012.08364 (2020).
4. Yuan, X. Generalized alternating projection based total variation minimization for compressive sensing. In 2016 IEEE International conference on image processing (ICIP),2539-2543 (IEEE, 2016).
5. Miao, X., Yuan, X., Pu, Y. & Athitsos, V. λ-net: reconstruct hyperspectral images from a snapshot measurement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 4059-4069 (IEEE, 2019).
论文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2709472323000084
关于Chip
Chip是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,已入选由中国科协、教育部、科技部、中科院等单位联合实施的「中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目」,为科技部鼓励发表「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。
Chip期刊由上海交通大学与Elsevier集团合作出版,并与多家国内外知名学术组织展开合作,为学术会议提供高质量交流平台。
Chip秉承创刊理念: All About Chip,聚焦芯片,兼容并包,旨在发表与芯片相关的各科研领域尖端突破性成果,助力未来芯片科技发展。迄今为止,Chip已在其编委会汇集了来自14个国家的70名世界知名专家学者,其中包括多名中外院士及IEEE、ACM、Optica等知名国际学会终身会士(Fellow)。
Chip第二卷第二期(2023年夏刊)即将于2023年6月在爱思维尔Chip官网以金色开放获取形式(Gold Open Access)发布,欢迎访问阅读本期最新文章。
爱思唯尔Chip官网:
https://www.journals.elsevier.com/chip




